Cp Vs Cv
This will help set realistic goals and aid in avoiding unnecessary pressure to the bodies involved in the process.
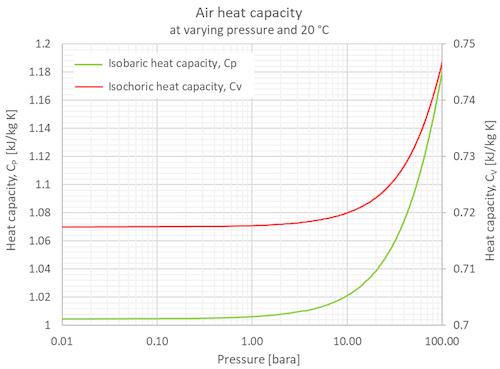
Cp vs cv. Isobaric specific heat c p is used for air in a constant pressure dp 0 system. Now you begin with the gas at atmospheric pressure 760 torr and then add gas to increase the pressure inside the bottle by a small amount say 15 114 torr. However they are all functions of temperature and with the extremely high temperature range experienced in internal combustion and gas turbine engines one can obtain significant errors. As per my understanding when you are writing the ener.
At constant volume the molar heat capacity c is represented by c v. In any industry understanding the true potential of a process is vital. The demand must be realistic and it should be certain that it is viable and the process is capable of achieving it. Cv is the specific heat at constant volume and cp is the specific heat at constant pressure.
In thermal physics and thermodynamics the heat capacity ratio also known as the adiabatic index the ratio of specific heats or laplaces coefficient is the ratio of the heat capacity at constant pressure c p to heat capacity at constant volume c vit is sometimes also known as the isentropic expansion factor and is denoted by g for an ideal gas or k the isentropic exponent for a. Since you didnt ask me about defination of cp and cv what most of the writers have answered your question as per my understanding is why are they used in thermodynamic or energy equations. Isochoric specific heat c v is used for air in a constant volume isovolumetric or isometric closed system. Specific heat c is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a mass unit of a substance by one degree.
It is mayers equation. The nominal values used for air at 300 k are c p 100 kjkgk c v 0718 kjkgk and k 14. At normal atmospheric pressure of 1013 bar the specific heat of. Setup for measuring the ratio of cpcv for gases.
The molar heat capacity c at constant pressure is represented by c p. The specific heats of gases are given as cp and cv at constant pressure and constant volume respectively while solids and liquids are having only single value for specific heat. Cv and cp are two terms used in thermodynamics. Thermodynamics is a branch of physical chemistry that describes the relationship of heat energy with other forms of energy.
What are heat capacity c c p and c v. In this article we will discuss two types of molar heat capacity c p and c v and derive a relationship between cp and cv. Now very quickly pop the stopper from the bottleneck and return it very quickly to its original position figure 2.